Manual therapy treatment:
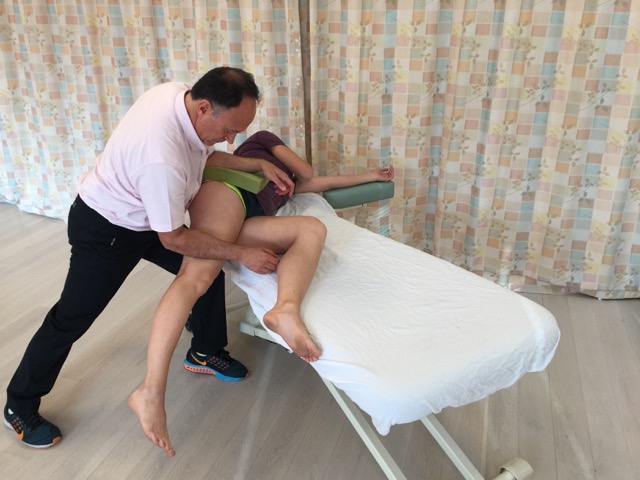
Manual therapy treatment for ITBFS is geared primarily toward reducing the inflammation of the condition and correcting its underlying cause. For the condition itself, ice is indicated to reduce the swelling. Gentle effleurage strokes from distal to proximal might also be helpful. Also, the client/patient should be advised to rest.
If the underlying cause is a tight ITB, then this needs to be corrected. Moist heat followed by soft tissue manipulation (massage), foam rolling, and stretching to the causative musculature (tensor fasciae latae, gluteus maximus, and/or vastus lateralis) is effective. Treatment directed at the underlying vastus lateralis will also treat the ITB itself. This is helpful toward reducing its tension and breaking up possible adhesions. If adhesions have built up in the ITB directly over the lateral femoral epicondyle, these manual techniques can and should be directed there as well; however, this is usually indicated in the later stages of care after the acute inflammation has dissipated. If the underlying cause is another musculoskeletal condition such as genu varum, genu valgum, or overpronation, then that condition must be addressed as well.
Summary of Manual Therapy Treatment Protocol for iliotibial band friction syndrome (ITBFS)
| 1. Ice and gentle distal-to-proximal effleurage |
| 2. Moist heat, soft tissue manipulation, foam rolling, and stretch to causative musculature as well as the ITB itself |
| 3. If genu valgus is present, strengthen the gluteus medius and minimus; loosen the adductor musculature |
| 4. Address genu varum or overpronation of the foot if present. |
Precautions/contraindications:
During the acute stage of ITBFS, nothing should be done that would increase swelling; therefore, any soft tissue manipulation should be gentle in force. If soft tissue manipulation is done distal to the knee joint, caution should be exercised so that excessive pressure is not placed over the common fibular nerve near the fibular head.